Multi-band police light source system
Basic structure and principle of multi-band light source
A multi-band light source is an optical system that divides the white light emitted by the light source into different bands by one or two sets of color filters, and then outputs it through a light guide. It mainly consists of five parts: light source, filter system, output system, control display system, and cabinet. (See Figure 1 for the structure). Among them, the light source, filter system, and output system are the core parts of the multi-band light source, which determine the performance of the light source. The light source generally adopts xenon lamp, indium light or other metal halide lamps with high luminous efficiency. The filter system mainly refers to the color filter, there are ordinary coated color filters or high-quality band-pass interference color filters. The performance of the latter is much better than that of the former, which mainly reduces the cut-off bandwidth of the colored light, that is, the monochromaticity of the colored light is greatly improved. The usual output wavelength coverage is 350~1000nm, including most of the spectral lines in the long-wave ultraviolet, visible light and near-infrared regions.
Application principle of multi-band light source
1. Fluorescence and multi-band light sources
When the extranuclear electrons are excited and jump to the excited state, the electrons in the excited state are unstable and always jump back to the ground state with lower energy. During the jump, the received energy will be released in the form of photons. . The phenomenon that a substance is excited to an excited state after being irradiated by a photon of a certain wavelength, and then jumps back to a lower energy level by releasing a photon of another specific wavelength
It is called photoluminescence phenomenon, and the photon lifetime usually released is less than 0.000001 second, which is called fluorescence; between 0.0001 and 0.1 second, it is called phosphorescence. If a substance can self-excite and produce fluorescence without external light excitation, it is said that the substance has intrinsic fluorescence. Another situation of fluorescence is to generate light waves with different wavelengths from the original light waves (usually short-wave excitations to generate long waves) under the excitation of an external light source, and the macroscopic manifestation is to emit another color light. The multi-band light source can provide not only an inverse light source for observing intrinsic fluorescence, but also an excitation light source.
2. Color separation principle
The principle of color separation is the prerequisite for the correct selection of the wavelength band (color light) and color filter of the multi-band light source. means that by selecting shades.
Forensic Multiband Light Source Filters
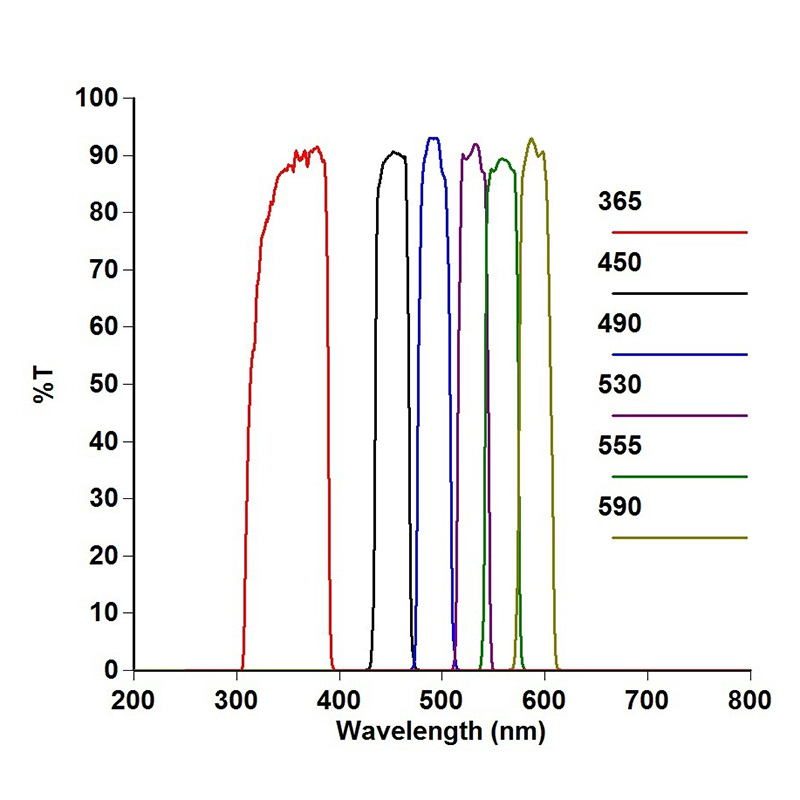
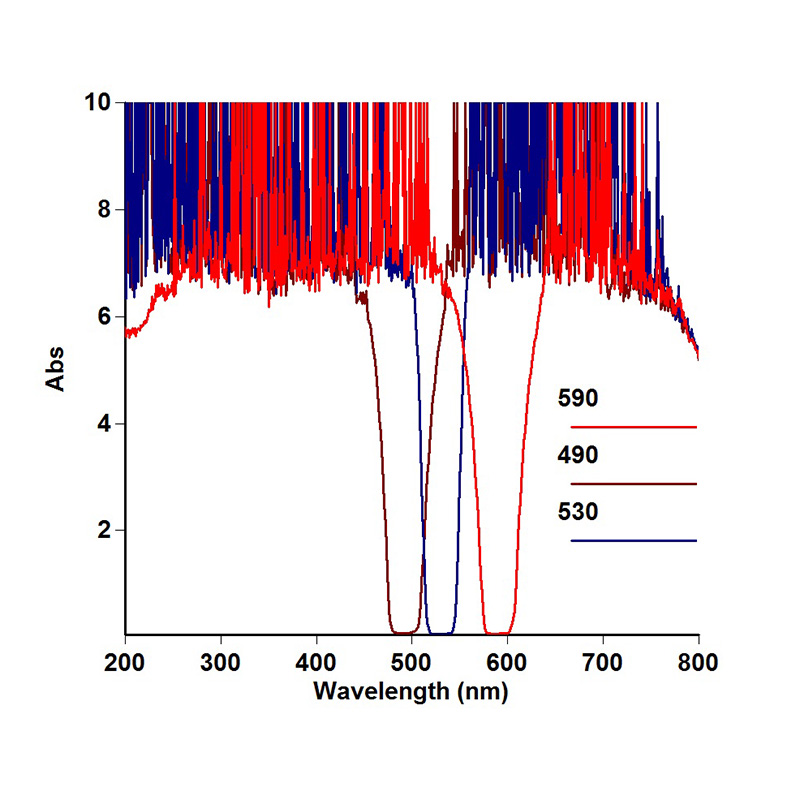
|
Process |
(IAD Hard Coating) |
|
Substrate |
Pyrex, Fused silicon |
|
FWHM |
30±5nm |
|
CWL(nm) |
365, 415, 450, 470, 490, 505, CSS510, 530, 555, 570, 590, 610 |
|
T avg. |
>80% |
|
Slope |
50%~OD5 < 10nm |
|
Blocking |
OD=5-6@200-800nm |
|
Dimension(mm) |
Φ15, Φ21.2, Φ25, Φ55, etc. |
Production Proces